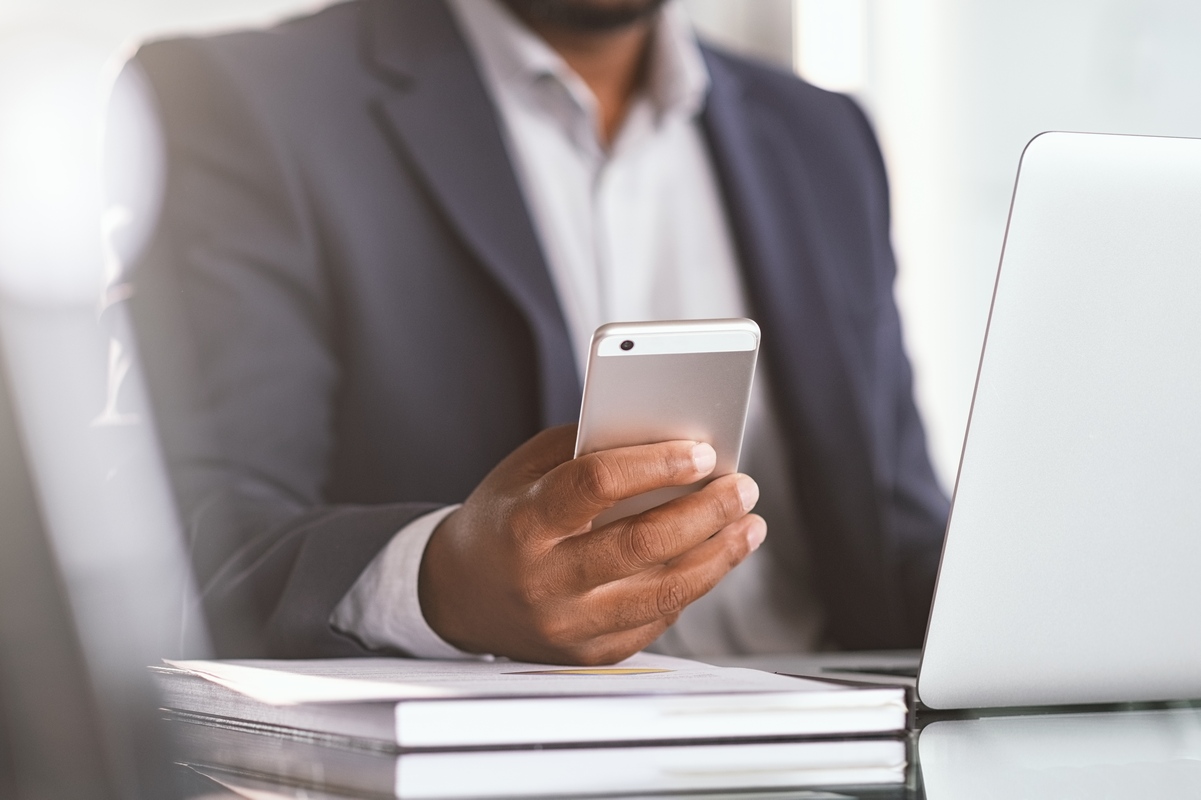
Having an ironclad mobile device management plan is essential for your company’s security. Device theft, loss, and malware attacks all pose a significant risk to your business; accordingly, providing your employees with a usage policy that promotes security and accountability is the best way to keep your company and your staff safe. Let’s take a closer look at eight useful practices to include in your mobile device management plan:
Report loss or theft immediately.
Employees should always report lost or stolen mobile devices through the appropriate channels immediately. Whether you handle your IT needs in-house or work with a Managed IT Services Provider (MSP), establish a procedure and contact person that employees can reach when things go wrong. Quick reporting allows your IT team to lock devices and/or erase sensitive information, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot gain access to proprietary or personal data. Many companies also choose to enable location services, which can help them locate devices that have gone missing.
Require employees to use passcodes and passwords.
Requiring employees to use passcodes is one of the simplest best practices for mobile device management. Employees should set a passcode that is not easy to guess (“123456” or “121212” are easy targets for any criminal trying to access a stolen phone or iPad). Employees should also ensure that the passwords they use to access any proprietary data or applications on their devices are challenging to guess – they should incorporate FaceID, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and a random combination of numbers, letters, and characters that prevent hackers from succeeding. Passwords should also not be shared or reused.
Make software and OS updates mandatory.
Software updates often include patches, which address security loopholes or issues within software and operating systems. If employees neglect their updates, they could be unknowingly allowing attackers to gain entry to your business through zero-day vulnerabilities. Teach employees about the importance of updates, and require them to install updates as soon as they receive them.
Install mobile antivirus software.
While mobile devices are largely safe from traditional computer-based viruses, malware can still affect phones, tablets, and other important equipment. This is especially true for rooted or jail-broken devices, which should be prohibited on your company’s network. For all other devices, installing a mobile-specific antivirus software can help keep your company’s data safe from attackers. These programs scan attachments for viruses, optimize device performance, and help identify threats like phishing attacks.
Only allow employees to install approved applications.
Work with your IT team or MSP to define a list of approved applications for company use. This can become complicated if you offer a bring your own device (BYOD) policy for employees, so working with professionals in this area can be helpful. If your employees only use company-issued devices, your IT team will be able to block and/or disable any third-party applications that could pose a threat to your business.
Remind employees to stay off of public WiFi and USB ports.
Employees should refrain from connecting to public WiFi. Unsecured public networks are a breeding ground for malicious threats like malware. If your employees connect to these networks and have sensitive information on their devices, hackers may be able to gain entry to your company’s network and do significant damage. Public USB ports often used for charging can also deliver malware to a mobile device, so employees should use a traditional outlet charger instead.
Train employees on mobile device management regularly.
Help your employees understand the seriousness of cybersecurity threats by training them on mobile device management at consistent intervals. Leverage touchpoints like onboarding and quarterly meetings to go over the essentials of mobile device security. As your device management plan changes and evolves, keep employees informed and trained to maximize the safety of your company and your staff.
Perform regular backups.
Backing up information is one of the most important methods of protecting data, especially if your employees store any important data on their phones or tablets. If a cybercriminal is able to infiltrate your network and unleash a ransomware attack, your company’s most sensitive and important data can be seized, encrypted, and possibly even irreversibly corrupted. Keeping your data backed up in a secure location can ensure your company will not face a total data loss, which can be catastrophic.
Conclusion
Your employees are often your last line of defense against threats to your business. Help them keep your business secure with an up-to-date mobile device management policy that lays out these critical best practices. If you are looking for ways to update or optimize your mobile device management plan, contact Qnectus today to start a conversation.